Modified True/False
Indicate
whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the
statement true.
|
|
|
1.
|
As water waves enter a deeper medium, they speed up and their wavelength
shortens. _________________________
|
|
|
2.
|
The angle of incidence equals the angle of refraction.
_________________________
|
|
|
3.
|
The angle of incidence can be measured between the incident wave front and the
boundary. _________________________
|
|
|
4.
|
Total internal reflection occurs when the incident angle is equal to the
critical angle. _________________________
|
|
|
5.
|
Higher frequencies of sound bend through a doorway more easily.
_________________________
|
|
|
6.
|
Michelson's interferometer was used to disprove the existence of an
“ether” filling all of space. _________________________
|
|
|
7.
|
For diffraction to be observable, the slit width w must be greater
than or equal to the wavelength l.
_________________________
|
|
|
8.
|
Nodal lines occur at points of continual constructive interference.
_________________________
|
|
|
9.
|
It is generally accepted that light exhibits only wave properties.
______________________________
|
|
|
10.
|
In light, longer wavelengths refract less than shorter wavelengths.
_________________________
|
|
|
11.
|
When white light passes through a diffraction grating, red light is
deflected least. _________________________
|
|
|
12.
|
When light rays pass from a more dense layer (i.e., a soap bubble) into air, the
phase is unaffected. _________________________
|
|
|
13.
|
The wave equation, 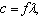 applies to all forms of EM waves.
_________________________
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
14.
|
A ripple tank is used to generate water waves. These waves are refracted as they
travel from deep to shallow water. Which of the following factors, when changed, will not affect the
amount of bending observed?
a. | the angle between the boundary and the incident wave front | b. | the difference in
depth between the shallow and deep regions | c. | the wavelength of the incident
wave | d. | the amplitude of the incident wave | e. | the frequency of the incident
wave |
|
|
|
|
|
|
15.
|
The diagram above shows a series of wave fronts travelling in a ripple tank from
a deep portion to a shallow portion of the tank. The angle of incidence for the above case is
a. | 70o | d. | 30o | b. | 50o | e. | 20o | c. | 40o |
|
|
|
16.
|
A narrow beam of monochromatic light enters diamond from air at an incident
angle of 65o. If the speed of light in air is 3.00 ´
108 m/s and the speed of light in diamond is 1.24 ´
108 m/s, the angle of refraction is
a. | 65o | b. | 25o | c. | 22o | d. | indeterminable but larger than
65o | e. | nonexistent since total internal reflection occurs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
17.
|
A series of wave fronts in a wave tank travelling toward an opening are shown
above. You wish to decrease the amount of visible diffraction by considering the following
changes: I. increase the depth of the
water
II. increase the size of the
opening
III. increase the frequency of the source
Which of
the above changes, or combination of changes, would decrease the diffraction most? a. | I only | d. | I and II only | b. | II only | e. | II and III only | c. | III
only |
|
|
|
18.
|
In the diagram below (not to scale), Two point sources, S 1 and
S 2, are located 6.0 cm apart, vibrating in phase, and producing waves of wavelength 1.25
cm. If point Q is located on the second nodal line a distance of 24 cm from O, then the distance from
M to Q is 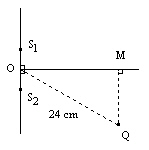 a. | 2.5 cm | d. | 12 cm | b. | 5.0 cm | e. | 15 cm | c. | 7.5
cm |
|
|
|
|
|
|
19.
|
The diagram above shows two identical speakers arranged at ear level. They are
emitting the same frequency in phase. The speakers are 3.0 m apart and an observer stands 4.0 m
directly in front of one speaker at point X. The sound intensity will be least for the observer at X
when the wavelength of the sound is
a. | 5.0 m | d. | 2.0 m | b. | 4.0 m | e. | 1.0 m | c. | 3.0
m |
|
|
|
20.
|
A two-point source interference pattern is generated in a ripple tank by
identical sources vibrating in phase and located 12.0 cm apart. There are seven nodal lines observed
on each side of the centre line. If the frequency of the sources is doubled and they remain in
phase
a. | the number of nodal lines observed will double | b. | the wavelength
doubles | c. | the speed of the wave doubles | d. | the number of nodal lines will decrease to
half | e. | the average distance between nodal lines increases |
|
|
|
21.
|
Consider the following properties of light: I. rectilinear
propagation
II. reflection
III.
refraction
IV. diffraction
V.
partial reflection-refraction
Which of these properties did Huygens have trouble explaining
with his theory of light? a. | I only | b. | IV only | c. | I and IV
only | d. | I and V only | e. | All of these properties can be explained using
Huygens’ theory. |
|
|
|
22.
|
The assumption that light particles have an extremely small mass and travel at
very high speeds was needed by Newton to explain
a. | rectilinear propagation | d. | partial reflection–partial
refraction | b. | diffraction | e. | reflection | c. | refraction |
|
|
|
23.
|
Which of the following properties of light cannot be explained by the particle
theory but can easily be explained by the wave theory?
a. | rectilinear propagation | d. | dispersion | b. | transmission in a
vacuum | e. | diffraction | c. | refraction |
|
|
|
24.
|
Point A is located 2.0 m horizontally away from point B. A ray of light is seen
to travel in a straight line from point A to point B. A small projectile is launched at 25 m/s from
point A and follows a parabolic path and strikes a point located below point B. To accept the
particle model of light based only on this observation, it must be concluded that the light
particles
a. | have a very small kinetic energy compared to the projectile | b. | have a very small
momentum compared to the projectile | c. | are travelling much, much faster than 25
m/s | d. | have a very small mass | e. | cannot adequately explain this
observation |
|
|
|
25.
|
The behaviour of light is often described using the wave theory because
a. | Einstein, a prominent physicist, supported this theory | b. | light waves can
easily be observed in a laboratory setting | c. | light behaves like a wave | d. | all of the
properties of light can be explained using a wave model | e. | many of the
properties of light can be explained using a wave model |
|
|
|
26.
|
Two small light bulbs are placed close together to try and create an
interference pattern. This pattern would not be visible due to the
a. | random phase differences between the light waves from the two
sources | b. | very high speed of the light waves | c. | diffraction of the light through the air
molecules surrounding the bulbs | d. | very short wavelengths of the light
waves | e. | inability of the human eyes to resolve two sources close
together |
|
|
|
27.
|
A student performs a double-slit experiment using two slits spaced 0.20 mm apart
and located 1.50 m from the screen. The monochromatic light source creates an interference pattern in
which the average distance between dark bands is 0.45 cm. What is the wavelength of the light being
used?
a. | 6.0 ´ 10–9 m | d. | 6.0 ´ 10–5 m | b. | 6.0 ´
10–8 m | e. | 15
m | c. | 6.0 ´ 10–7
m |
|
|
|
28.
|
A student performs a double-slit experiment using a monochromatic light source,
two slits spaced 0.10 mm apart, and a screen located 150 cm away. The bright fringes are located 0.30
cm apart. If the distance between the slits was changed to 0.20 mm, what would the average distance
between bright fringes become?
a. | 0.15 cm | d. | 0.60 cm | b. | 0.30 cm | e. | 1.5 m | c. | 0.50
cm |
|
|
|
29.
|
A student performs a double-slit experiment using a monochromatic light source
with a wavelength of 5.00 ´ 10–7 m. The pattern
appears on a screen 150 cm away and the bright fringes are 0.40 cm apart. If the wavelength of the
light used is changed to 7.50 ´ 10–7 m, what would
the average distance between bright fringes become?
a. | 0.15 cm | d. | 0.60 cm | b. | 0.20 cm | e. | 1.5 m | c. | 0.27
cm |
|
|
|
30.
|
A student performs a double-slit experiment using two slits spaced 0.25 mm apart
and located 3.0 m from a screen. Infrared light with a wavelength of 1200 nm is used and film
sensitive to infrared light is used as the screen. What is the average distance between adjacent dark
bands on the exposed film?
a. | 2.8 m | d. | 2.8 cm | b. | 1.4 m | e. | 1.4 cm | c. | 14
cm |
|
|
|
31.
|
A double-slit experiment is performed to measure the wavelength of a
monochromatic light source. It is found that the nodal lines are too close together to be easily
observed. Consider the following changes: I. the slit separation is
increased
II. the distance between the slits and the source is
increased
III. the distance between the slits and the screen is
increased
IV. the wavelength of the light is increased
The
best combination of the above changes which would increase the average distance between the nodal
lines observed is a. | I and II only | d. | II only | b. | III and IV only | e. | I, III, and IV only | c. | I
only |
|
|
|
32.
|
The speeds of red and blue light are compared to one another in glass and also
to their speeds in a vacuum. Which of the following statements is correct?
a. | Red light travels faster than blue light in glass, and both travel faster in glass
than in a vacuum. | b. | Red light travels faster than blue light in
glass, and both travel slower in glass than in a vacuum. | c. | Red light travels
the same speed as blue light in glass, and both travel slower in glass than in a
vacuum. | d. | Red light travels slower than blue light in glass, and both travel faster in glass
than in a vacuum. | e. | Red light travels slower than blue light in
glass, and both travel slower in glass than in a vacuum. |
|
|
|
33.
|
In which of the following can the property of polarization not be used?
a. | analyze the stress distribution in materials | b. | improve picture
quality in photography | c. | reducing glare from the Sun | d. | identifying solution
concentrations | e. | measuring very small distances using interference
patterns |
|
|
|
34.
|
Light from a monochromatic source shines on a single, narrow slit. Which of the
intensity patterns shown below best illustrates the interference pattern observed?
|
|
|
35.
|
An experiment using a diffraction grating with a monochromatic light source is
performed to create an interference pattern on a screen. Consider the following changes: I. Decrease the line density of the
grating.
II. Increase the frequency of the
source.
III. Decrease the distance to the screen.
Which of
these changes would cause the pattern to spread out? a. | I only | b. | III only | c. | I and III
only | d. | I, II, and III | e. | None of these changes would cause the pattern
to spread out. |
|
|
|
36.
|
Monochromatic light strikes a thin film normal to the surface. To obtain the
first bright reflected maximum, the thickness of the film must be
a. | much less than 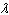 | d. | 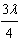 | b. | 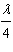 | e. | 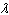 | c. | 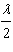 |
|
|
|
37.
|
Cameras are often comprised of several lenses laminated together. To maximize
the transmitted light, the lenses are often coated with a thin film, as shown below. 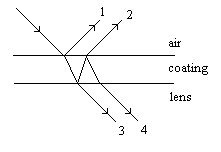 The condition required to maximize the amount of transmitted light is a. | Constructive interference must occur between light rays 1 and 2. | b. | The coating must be
more transparent than the lens. | c. | Destructive interference must occur between
light rays 3 and 4. | d. | The speed of the light must be lower in the
coating than in the lens. | e. | The total light energy reflected must be
minimized. |
|
|
|
38.
|
The main difference between normal photographic images and holographic images is
that
a. | Special viewing glasses are needed to properly see holograms. | b. | A camera uses a lens
to focus only a certain scene while a hologram captures all the light reflecting from the
object. | c. | Holograms can only be created using laser light. | d. | Holographic pictures
can only be created using light in the visible portion of the spectrum. | e. | Normal pictures can
only be created using light in the visible portion of the spectrum. |
|
Matching
|
|
|
Match the following phrases with the most appropriate choice below. Note that
not all phrases will be used. a. | leading edge of a continuous crest or trough | b. | particles in the
medium move parallel to the energy propagation direction | c. | property that allows
light to create sharp shadows | d. | violet light bends least due to this
phenomenon | e. | resultant waveform amplitude is zero (also called a minimum) | f. | particles in the
medium move perpendicular to the energy propagation direction | g. | resultant waveform
amplitude is larger (also called a maximum) | h. | indicates the direction of energy
transmission | i. | reference line drawn perpendicular to a surface | j. | well supported by
both the wave and particle theory of light | k. | red light bends least due to this
phenomenon |
|
|
|
39.
|
transverse wave
|
|
|
40.
|
wave ray
|
|
|
41.
|
refraction
|
|
|
42.
|
diffraction
|
|
|
43.
|
normal
|
|
|
44.
|
constructive interference
|
|
|
45.
|
nodal line
|
|
|
46.
|
rectilinear propagation
|
|
|
Match the following phrases with the most appropriate choice below. Note that
not all phrases will be used. a. | exists only if a wave is speeding up | b. | used to reveal
stress distribution within a material | c. | caused when waves pass through very small
openings | d. | composed of only one colour, or wavelength | e. | ability of an
optical instrument to separate two images located close together | f. | vibrations of a wave
are confined to a single plane | g. | ability of a substance to rotate the plane of
polarization of transmitted light | h. | caused when the index of refraction of a
substance depends on the wavelength | i. | used to properly conduct all experiments and
research | j. | all waves from the source are in phase with each other | k. | must explain current
observations and predict new behaviours |
|
|
|
47.
|
monochromatic
|
|
|
48.
|
critical angle
|
|
|
49.
|
scientific theory
|
|
|
50.
|
polarization
|
|
|
51.
|
resolution
|