Modified True/False
Indicate
whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the
statement true.
|
|
|
1.
|
In SI base units, the joule (J) is equivalent to 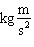 .
_________________________
|
|
|
2.
|
The work done in lifting an object without acceleration from the ground to some
height is slightly less than the object’s gain in gravitational potential energy during
the lift. _________________________
|
|
|
3.
|
For an ideal spring, the force-stretch graph is a curved line.
_________________________
|
|
|
4.
|
The area under a force-stretch graph of an ideal spring represents
the spring’s force constant. _________________________
|
|
|
5.
|
When calculating an object’s gravitational potential energy at a
particular location, it is essential to state a reference level.
_________________________
|
|
|
6.
|
A moon rock is thrown across the lunar surface. At all positions in the flight,
its total mechanical energy is a constant. _________________________
|
|
|
7.
|
Work is done when the force and the displacement are in the same
direction. _________________________
|
|
|
8.
|
The maximum work a force can do on an object occurs when the force is
parallel to the direction of motion. _________________________
|
|
|
9.
|
If you raise an object above your head and then set it on a table, you do the
same work as if you only lifted the object onto the table. ______________________________
|
|
|
10.
|
A group of three balls at the top of three different frictionless ramps drop the
same vertical distance with the same final speed regardless of the shape of the ramp.
_________________________
|
|
|
11.
|
Momentum is not conserved in all collisions.
_________________________
|
|
|
12.
|
It is possible that an object can receive a larger impulse from a small
force than from a large force. _________________________
|
|
|
13.
|
A single train car loaded with sand travels by itself along a horizontal
frictionless track at a constant speed. A hole is punctured in the bottom of train and the sand
slowly leaks out causing the train car to speed up. _________________________
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
14.
|
Work is
a. | energy transferred to an object | c. | the product of force and
distance | b. | energy transferred from an object | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
15.
|
Work is measured in joules when force and distance are respectively measured
in
a. | newtons and centimetres | c. | grams and
metres | b. | kilograms and centimetres | d. | newtons and metres |
|
|
|
16.
|
How far does a 5.0-N force have to move a 2.0-kg object to accomplish 24 J of
work?
a. | 4.8 m | c. | 2.4 m | b. | 3.4 m | d. | 0.42 m |
|
|
|
17.
|
If a toy car loses 8.4 J of kinetic energy by rolling across the floor for 1.5
m, the force of kinetic friction acting on the car has a magnitude of
a. | much greater than 5.6 N | c. | exactly 5.6 N | b. | slightly greater
than 5.6 N | d. | slightly more
than 5.6 N |
|
|
|
18.
|
If a person performs 6.1 J of work to lift an object without acceleration to a
particular height on Earth, how much energy is required for the same lift on the moon where the value
of g is 1.6 N/kg?
a. | This can’t be answered without knowing the mass of the
object. | b. | This can’t be answered without knowing the height of the
lift. | c. | This can’t be answered without knowing the mass of the object and the height of
the lift. | d. | 1.0 J |
|
|
|
19.
|
An astronaut performs 27.2 J of work to lift a 5.0-kg object without
acceleration to a height of 1.6 m on a distant planet. What is the value of the gravitational
constant, g, on that planet?
a. | 85 N/kg | c. | 8.7 N/kg | b. | 9.8 N/kg | d. | 3.4 N/kg |
|
|
|
20.
|
The force-stretch graph for an ideal spring
a. | is always a straight diagonal line | b. | is always a horizontal line | c. | is always a curved
line sweeping up and to the right | d. | may be a combination of straight and curved
sections |
|
|
|
21.
|
The gravitational potential energy of an object at some position relative to a
particular reference level is equivalent to
a. | the work done in lifting the object from the reference level to that
position | b. | the loss of kinetic energy of the object in reaching that
position | c. | the kinetic energy of the object at that position | d. | the gain in kinetic
energy of the object in reaching that position |
|
|
|
22.
|
A soccer ball of mass 665 g is kicked from the ground and gains 41 J of
gravitational potential energy as it reaches its maximum height of
a. | 62 m | c. | 1.7 m | b. | 6.3 m | d. | 0.16 m |
|
|
|
23.
|
A penny is dropped from the roof of a building. When it reaches a position
three-quarters of the way to the ground
a. | it has lost one quarter of its original gravitational potential
energy | b. | it still has one quarter of its original gravitational potential
energy | c. | if air resistance is considered, it has less than one quarter of its original
gravitational potential energy | d. | if air resistance is considered, it has more
than one quarter of its original gravitational potential energy |
|
|
|
24.
|
A 185-g arrow is shot vertically upward with a speed of 23 m/s. If air
resistance is neglected, what maximum height above its point of projection will the arrow
reach?
a. | 1.1 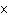 102 m 102 m | c. | 10 m | b. | 27
m | d. | 4.7
m |
|
|
|
25.
|
Two springs of identical mass are stretched the same amount and then launched
vertically upward. Which of the following statements is true?
a. | The spring with the greater force constant will reach a greater
height. | b. | The spring with the lesser force constant will reach a greater
height. | c. | The spring with the lesser force constant will have a greater speed upon
launch. | d. | The spring with the lesser force constant will require more force to stretch
it. |
|
|
|
26.
|
The gravitational potential energy of a 3.4-g grasshopper 14 mm above the ground
is
a. | 4.7 ´ 102 J | d. | 4.7 ´ 10–2 J | b. | 4.7 J | e. | 4.7 ´
10–4 J | c. | 0.47 J |
|
|
|
27.
|
You raise a 1.00-kg object 1.00 m and then lower it 1.00 m. The total work done
on the object by gravity is
a. | 0 J | d. | 19.6 J | b. | 9.8 J | e. | –19.6 J | c. | –9.8
J |
|
|
|
28.
|
To maximize the gravitational potential energy of an object, you should
a. | raise it as quickly as possible | d. | get it as high as
possible | b. | maximize the total distance travelled | e. | lower it in the vertical
direction | c. | avoid acceleration during lifting |
|
|
|
29.
|
A 1.30-kg pendulum bob is pulled to the side, raising it 19.0 cm above its rest
position. After it is released, the maximum speed will be
a. | 0.616 m/s | d. | 6.16 m/s | b. | 1.93 m/s | e. | 37.2 m/s | c. | 3.72
m/s |
|
|
|
30.
|
A horizontal spring, with a force constant of 39 N/m, is compressed 12.4 cm, and
placed between a wall and a 0.17-kg box resting on a smooth floor. If the spring is released, the
maximum speed of the box is
a. | 1.9 m/s | d. | 5.3 m/s | b. | 2.7 m/s | e. | 28 m/s | c. | 3.5
m/s |
|
|
|
31.
|
A spring-powered SHM oscillator vibrates with a period of 0.29 s. If the force
constant of the spring is 180 N/m, the mass used is
a. | 0.38 kg | d. | 2.4 kg | b. | 0.77 kg | e. | 2.6 kg | c. | 1.3
kg |
|
|
|
32.
|
If the mass of a car is doubled and its speed is cut in half, then the kinetic
energy changes by a factor of
|
|
|
33.
|
A rocket triples its height but looses half its mass in fuel. The gravitational
potential energy of the rocket has changed by a factor of
|
|
|
34.
|
A person runs at a constant speed up a slope that is angled at 12° to the horizontal. At one point, he is 3.2 m vertically above the bottom
of the hill. To double the gravitational energy compared to the bottom of the hill, the runner must
run an additional
a. | 0.66 m up the slope | d. | 6.4 m up the slope | b. | 1.6 m up the slope | e. | 15 m up the slope | c. | 3.2 m up the
slope |
|
|
|
35.
|
A crane exerts a force of 4.8 ´ 105 N
to lift a steel beam 15 m into the air in 18 s. If the time taken was 36 s, the energy required would
change by a factor of
|
|
|
36.
|
You want to ride a bicycle to the house shown below. Neglecting friction, at
which point should you start in order to use the least amount of work to get there?
|
|
|
37.
|
A 1.5-kg bird is flying west at a velocity of 18 m/s [22º above the
horizontal]. The horizontal component of its momentum is
a. | 10 m/s [W] (2 significant digits) | d. | 17 m/s
[W] | b. | 6.7 kg×m/s [W] | e. | 17 kg×m/s
[E] | c. | 25 kg×m/s
[W] |
|
|
|
38.
|
A shell is fired from a gun mounted on a battleship. Which of the following
statement is NOT true?
a. | There will be a force to push the boat in the opposite direction of the
shell. | b. | The recoil spring on the barrel is to minimize the force on the deck of the
ship. | c. | Neglecting fluid friction, the momentum of the boat and shell have the same
magnitude. | d. | To calculate the speed of the boat we would need to know the recoil length of the
gun. | e. | A larger mass of shell will increase the recoil force felt by the
ship. |
|
|
|
39.
|
A boy throws a 15-kg ball at 4.7 m/s to a 65-kg girl who is stationary and
standing on a skateboard. After catching the ball, the girl is travelling at
a. | 0 m/s | d. | 3.2 m/s | b. | 0.88 m/s | e. | 4.7 m/s | c. | 1.1
m/s |
|
|
|
40.
|
A goalie standing on a frictionless surface catches a 270.0-g puck travelling at
95.0 km/h. After catching the puck, the goalie is moving at 8.90 cm/s. The mass of the goalie
(including equipment) is
a. | 75.2 kg | d. | 84.2 kg | b. | 79.8 kg | e. | 91.7 kg | c. | 80.1
kg |
|
|
|
41.
|
A 72-kg girl on a skateboard doubles her kinetic energy coasting down a
hill.
a. | Momentum is conserved. | b. | The increase in kinetic energy is offset by a
decrease in momentum. | c. | The momentum will also
double. | d. | Her momentum does not change. | e. | none of the
above |
|
|
|
42.
|
A gun is mounted on a wooden plank. The plank is stationary and is mounted on
frictionless wheels. A heavy wooden block is set in front of the gun, and the gun is fired into the
wooden block, which then slows to a stop due to friction between the block and the plank.
a. | The plank does not move. | b. | Momentum is not conserved because of the
frictional force. | c. | The speed of the plank is zero immediately
after the collision between the bullet and block. | d. | The plank will have shifted position relative
to its starting point. | e. | Kinetic energy is conserved because the speed
of the system is zero before and after the collision. |
|
|
|
43.
|
A 5.0-kg cat travelling at 1.3 m/s [E] has a momentum of
a. | 6.5 m/s [E] | d. | 3.8 m/s [W] | b. | 6.5 m/s
[W] | e. | none of the
above | c. | 3.8 m/s [E] |
|
|
|
44.
|
A bullet with a momentum of 2.8 kg×m/s
[E] is travelling at a speed of 187 m/s. The mass of the bullet is
a. | 0.015 g | d. | 67 g | b. | 0.067 g | e. | not enough information | c. | 15
g |
|
Matching
|
|
|
Match each form of energy with its corresponding description listed
below. a. | chemical potential energy | e. | electrical
energy | b. | sound energy | f. | gravitational potential energy | c. | radiant energy | g. | kinetic energy | d. | nuclear
energy | h. | elastic potential
energy |
|
|
|
45.
|
this is possessed by all moving objects
|
|
|
46.
|
visible light as well as all members of the electromagnetic spectrum are
examples of this
|
|
|
47.
|
when atoms split (fission) or combine (fusion) this is released
|
|
|
48.
|
objects possess this type of energy by being elevated above some reference
level
|
|
|
49.
|
a stretched or compressed spring will have this type of stored energy
|
|
|
50.
|
this type of energy, produced by vibrations, must travel through some material
to be transmitted
|
|
|
51.
|
this type of energy is absorbed and released when atoms combine to form
molecules
|
|
|
52.
|
electrons deliver this type of energy from the battery to the light bulb in a
simple flashlight circuit
|
|
|
Match each of the following examples with the value of the work done on the
object underlined in each case. a. | positive work | b. | negative work | c. | zero
work |
|
|
|
53.
|
A person exerts an applied force on a spring that results in the spring
being stretched.
|
|
|
54.
|
A person exerts an applied force on a spring that results in the spring
being compressed.
|
|
|
55.
|
The force of kinetic friction acts on a sliding puck, eventually
bringing the puck to rest.
|
|
|
56.
|
The force of gravity accelerates an apple as it falls to the
ground.
|
|
|
57.
|
A truck bed exerts a normal force upward on a crate as the truck moves
horizontally.
|
|
|
58.
|
A bungee cord exerts an applied force on a person as the person is
falling.
|
|
|
59.
|
A person exerts an applied force on a massive object, but the object
does not move.
|