Modified True/False
Indicate
whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the
statement true.
|
|
|
1.
|
If electrons are added to an object, it will be charged negatively.
_________________________
|
|
|
2.
|
Coulomb’s law is extremely accurate under the conditions that the spheres
are small and that the spheres are also small compared to the distance between them.
______________________________
|
|
|
3.
|
When the charge on both spheres is doubled, the electric force is increased
by a factor of four. _________________________
|
|
|
4.
|
One of the ways in which Newton’s law of universal gravitation differs
from Coulomb’s law is that gravitational force can only attract, whereas the electric force
can only repel. ________________________________________
|
|
|
5.
|
If q1 and q2 are opposite charges, they
attract and the electric potential is a negative value, as in the case of gravitational potential
energy. _________________________
|
|
|
6.
|
The unit of electric potential is joules per volt.
_________________________
|
|
|
7.
|
When the net force on an oil drop in a Millikan apparatus is zero, the
gravity downward cancels the product of the mass and the electric field on the oil drop.
__________________________________________________
|
|
|
8.
|
For a charge q1 moving in the electric field of
q2 in a vacuum, the loss of electric potential energy is equal to the gain
in kinetic energy. _________________________
|
|
|
9.
|
The relative strength of the magnetic field is indicated by the spacing of
adjacent field lines. The farther apart the lines, the stronger the magnetic field.
______________________________
|
|
|
10.
|
In two-dimensional diagrams of magnetic fields dots are drawn to
represent field lines pointing out of and perpendicular to the page.
______________________________
|
|
|
11.
|
The magnetic field around a straight conductor consists of field lines that are
concentric circles. The circles become more widely spaced as the distance from the conductor
decreases. _________________________
|
|
|
12.
|
Measurements of the magnetic field strength show that 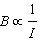 .
_________________________
|
|
|
13.
|
Measurements of the magnetic field strength have shown that 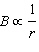 .
|
|
|
14.
|
The value of 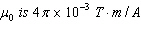 . _________________________
|
|
|
15.
|
A larger current is produced when a magnet is plunged into a solenoid by
increasing the number of turns in the coil. _________________________
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
16.
|
A negatively charged rod is held near, but does not touch the knob of an
electroscope. The leaves of the electroscope move apart from one another. A wire is connected to the
knob and to a water tap with the negatively charged rod staying in the same position. Which of the
following would occur?
a. | Electrons flow from the earth through the wire to the
electroscope. | b. | No electron flow takes place. | c. | The leaves of the electroscope remain
still. | d. | The leaves of the electroscope move closer together. | e. | Electrons flow from
the electroscope through the wire to the earth. |
|
|
|
17.
|
Solids in which electrons are able to move easily from one atom to another
are
a. | conductors | d. | neutral | b. | electrically charged | e. | capacitors | c. | insulators |
|
|
|
18.
|
Which of the following materials when rubbed against an aluminium zinc rod would
cause the greatest negative charge?
a. | cat’s fur | d. | cotton | b. | silk | e. | human hair | c. | wool |
|
|
|
19.
|
The electrostatic force between two point charges is 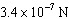 . If the distance between
the charges is tripled but the size of the charges remains the same, the force between them will
be
|
|
|
20.
|
Two charged spheres are 15.00 cm apart. One sphere has a charge of 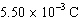 and
the other sphere has a charge of 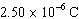 . Assuming k = 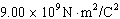 , the electric force
between the two spheres is
|
|
|
21.
|
Which of the following diagrams best illustrates the electric field in the area
around two identical charges?
|
|
|
22.
|
The diagram below shows two point charges, B and C, and the electric field lines
in the region around them. 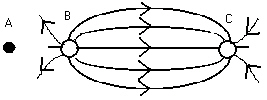 Which one of the following statements is true? a. | A negative point charge placed at point A will move toward the
left. | b. | The charges on both B and C are negative. | c. | The charges on both
B and C are positive. | d. | The electric field is strongest nearest point
B. | e. | A negative point charge placed at point A will move toward the
right. |
|
|
|
23.
|
Which of the following diagrams most accurately depicts the field between two
oppositely charged plates?
|
|
|
24.
|
An object with charge + q experiences an electric force
FE when put in a particular location in the electric field 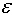 . The positive
charge + q is removed and an object with charge –4 q is placed in the same location
in the electric field. This charge would feel an electric force of
|
|
|
25.
|
If point charge + q was absent, the electric field at point B would be E.
What is the electric field between the two point charges, + q and – q, at point B
which lies at the midpoint between the two charges? 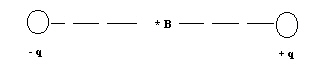 a. | 2E [right] | d. | 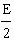 [left] [left] | b. | 0 | e. | 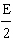 [right]
[right] | c. | 2E
[left] |
|
|
|
26.
|
The magnitude of the electric field between the plates of a parallel plate
capacitor is 4.7 ´ 104 N/C. If the plates were separated
to a distance that is twice their original separation distance, the magnitude of the electric field
would
a. | double | d. | decrease by a factor of sixteen | b. | be
halved | e. | not be
affected | c. | decrease by a factor of four |
|
|
|
27.
|
The sign of the electric potential difference depends on
a. | the sign of the charge | b. | the magnitudes of the distances from the
charge | c. | the magnitude of the electric potential of the positive plate | d. | the magnitude of the
electric potential of the negative plate and the distance between the plates | e. | the magnitude of the
distance from the charge and the sign of the charge |
|
|
|
28.
|
A 2.4 ´ 10–3-C positive test
charge is placed between two plates. The potential difference between two parallel metal plates is 30
V. Plate A is positive and plate B is negative. Which plate has a higher electric potential?
a. | plate A | b. | plate B | c. | Plates A and B have
the same potential. | d. | If the positive charge is placed closer to the
positive plate, then plate A will have a greater electric potential. | e. | If the positive
charge is placed closer to the negative plate, then plate B will have a greater electric
potential. |
|
|
|
29.
|
The electric field intensity between two parallel plates is 300.0 N/C. The
plates are connected to a battery with an electric potential difference of 12.0 V. The separation of
the plates is
a. | 25.0 m | d. | 4.0 ´ 10–7
m | b. | 3600.0 m | e. | 0.040 m | c. | 2.3 ´
1011 m |
|
|
|
30.
|
In his experiment, J.J. Thomson demonstrated that cathode rays are deflected by
a magnetic field. From this, we know that cathode rays
a. | contain potential energy | d. | carry a charge | b. | travel in straight
lines | e. | are affected by the
force of gravity | c. | travel at the speed of light |
|
|
|
31.
|
In his experiment, J.J. Thomson demonstrated that cathode rays are deflected by
an electric field. From this, we know that cathode rays
a. | possess potential energy | d. | are affected by the force of
gravity | b. | travel at the speed of light | e. | carry a charge | c. | travel in straight
lines |
|
|
|
32.
|
| | FM | 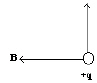 | | | | |
The direction of the
positively charged particle’s velocity according to the diagram above must be a. | to the left | b. | to the right | c. | upward | d. | out of the page, perpendicular to the
page | e. | into the page, perpendicular to the page |
|
|
|
33.
|
A 50.0-cm straight conductor carries a current of 10.0 A through a uniform
magnetic field. The magnitude of the force on the conductor is 0.50 N. The angle between the current
and the magnetic field is 50.0°. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field?
a. | 1.9 T | d. | 12 000 T | b. | 190 N | e. | 120 T | c. | 0.13
T |
|
|
|
34.
|
A conductor is located between the poles of a horseshoe magnet. Current flows in
the direction indicated by the arrow on the diagram. 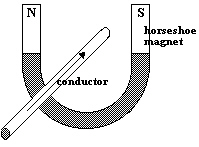 In which direction will the conductor
move? a. | upward | d. | right | b. | left | e. | out of the page | c. | downward |
|
|
|
35.
|
What is the magnetic field at point Y halfway between the two conductors in the
diagram below? 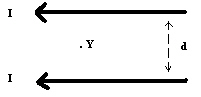 a. | zero | d. | 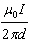 , into the page , into the page | b. | 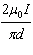 , out of
the page , out of
the page | e. | 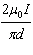 , into the
page , into the
page | c. | 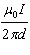 , out of the page , out of the page |
|
|
|
36.
|
Two parallel conductors 10.0 m long and 2.0 cm apart are to carry equal
currents. The force each conductor experiences due to the other is not to exceed 3.0 ´ 10–1 N. The maximum possible current in each conductor
is
a. | 7.5 ´ 108 A | d. | 3.0 ´ 103 A | b. | 6.0 ´
10–2 A | e. | 2.5
´ 10–1 A | c. | 5.5 ´ 101 A |
|
|
|
37.
|
A straight wire carrying a current of 2.0 A is next to another wire carrying a
current of 5.0 A. If the magnitude of the force between them is 4.5 ´
10–-2 N/m, then the distance between the wires is
a. | 4.4 ´ 10–5 m | d. | 4.5 ´ 10–1 m | b. | 7.1 ´
10–2 m | e. | 2.3 ´ 10–4 m | c. | 2.3 ´ 104 m |
|
|
|
38.
|
In the diagram below, a permanent magnet is pulled upward through a horizontal
loop of wire. 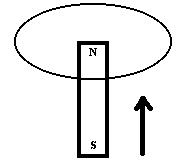 Which of the following describes the induced current as
viewed from above? a. | clockwise then counterclockwise | d. | counterclockwise | b. | clockwise | e. | No current is induced. | c. | counterclockwise
then clockwise |
|
|
|
39.
|
In the diagram below, a permanent magnet located above the loop is pushed
downward through the loop of wire. 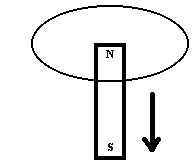 Which of the following describes the induced current as
viewed from above? a. | clockwise then counterclockwise | d. | counterclockwise | b. | clockwise | e. | No current is induced. | c. | counterclockwise
then clockwise |
|
Matching
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | law of electric charges | d. | induced charge
separation | b. | charging by contact | e. | charging by friction | c. | law of conservation of
charge |
|
|
|
40.
|
Some substances acquire an electric charge when rubbed with other
substances.
|
|
|
41.
|
The total charge within an isolated system remains the same.
|
|
|
42.
|
Opposite charges attract one another, similar charges repel one another, and
charged objects attract some neutral objects.
|
|
|
43.
|
A charged rod touches a neutral pith ball and some of the excess electrons move
to the pith ball.
|
|
|
44.
|
A negatively charged rod is brought near a neutral pith ball and many free
electrons are repelled to the far side of the pith ball.
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | field of force | e. | law of universal gravitation | b. | electric
field | f. | electrophoresis | c. | Coulomb’s law | g. | coaxial cable | d. | electrostatic
precipitator |
|
|
|
45.
|
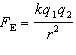
|
|
|
46.
|
used for cable TV and between stereo components
|
|
|
47.
|
used to separate large charged molecules
|
|
|
48.
|
object placed at any point in space and experiences attraction or
repulsion
|
|
|
49.
|
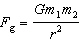
|
|
|
50.
|
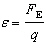
|
|
|
51.
|
removes tiny soot, ash, and dust particles
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | volts | d. | C | b. | joules | e. | e | c. | N/C |
|
|
|
52.
|
electric field intensity
|
|
|
53.
|
electric potential
|
|
|
54.
|
quantum of charge
|
|
|
55.
|
work
|
|
|
56.
|
charge
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | electric potential | d. | electric potential energy | b. | electric field
intensity | e. | kinetic
energy | c. | elementary charge |
|
|
|
57.
|
electric force per unit positive charge
|
|
|
58.
|
energy that increases as the distance between two charges of the same sign
increases
|
|
|
59.
|
energy a charge has when positioned a small distance from another charge of the
same sign; decreases as the distance between the charges increases
|
|
|
60.
|
charge on an electron
|
|
|
61.
|
work necessary to move a positive charge from rest at infinity to rest at a
point
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct unit below. a. | magnetic field strength | d. | magnetic force | b. | current | e. | charge | c. | potential
difference |
|
|
|
62.
|
newton
|
|
|
63.
|
coulomb
|
|
|
64.
|
tesla
|
|
|
65.
|
volt
|
|
|
66.
|
ampere
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | coulomb | d. | 9.1 ´ 10–31
kg | b. | ampere | e. | FM | c. | 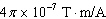 | f. | 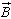 |
|
|
|
67.
|
newton/metre
|
|
|
68.
|
ampere·second
|
|
|
69.
|
mass of an electron
|
|
|
70.
|
magnetic force
|
|
|
71.
|
permeability of free space 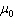
|
|
|
72.
|
magnetic field strength
|