True/False
Indicate whether the
statement is true or false.
|
|
|
1.
|
The reason your head feels like it jerks backward when pulling away from a stop
sign is best explained by Newton's First Law.
|
|
|
2.
|
An airplane is flying in level flight with constant velocity. The forward
"thrust" force acting on the airplane is greater than the "drag" force acting in
the opposite direction.
|
|
|
3.
|
If the vector sum of all forces acting on an object is precisely zero, the
object could still be moving.
|
|
|
4.
|
A geostationary satellite that transmits television signals to home satellite
dishes is under the influence of perfectly balanced forces.
|
|
|
5.
|
When drawing a proper free-body diagram, all forces, including the net force
acting on the object, must be clearly indicated.
|
|
|
6.
|
If the supporting cables of an elevator snapped and the elevator began falling,
the passengers would become trapped against the ceiling of the elevator provided there is no air
resistance or friction in the elevator shaft.
|
|
|
7.
|
A person pulls on one end of a rope whose other end is firmly tied to a sturdy
pole. The force exerted by the person is not quite strong enough to break the rope. If the end is
then untied from the pole and two people pull on opposite ends, each with a force identical to the
person in the first case, the rope may break.
|
|
|
8.
|
Two people pushing an object against friction across a surface will result in
twice the acceleration than if only one person pushes. Assume that the object slides in both cases
and that both people push with the same force.
|
|
|
9.
|
An object in orbit around Earth only appears weightless when it is actually free
falling along with everything around it.
|
|
|
10.
|
For any pair of surfaces, the coefficient of static friction between the
surfaces is less than the corresponding coefficient of sliding friction.
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
11.
|
A stone is tied to the end of a string and twirled around in a circle which
describes a vertical plane. Which of the following free-body diagrams best represents the forces
acting on the stone at the top of the circle? 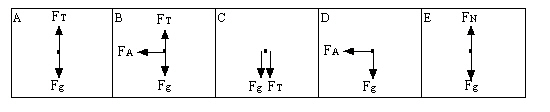
|
|
|
12.
|
How much force would you have to apply to just support the weight of an average
apple of mass 1.0 ´ 102 g?
a. | 9.8 ´ 103 N [up] | d. | 9.8 ´ 100 N [up] | b. | 9.8 ´ 102 N [up] | e. | 9.8 ´
10–1 N [up] | c. | 9.8 ´
101 N [up] |
|
|
|
13.
|
Which of the following observations is explained by Newton's first
law?
a. | kicking your feet against something solid to remove snow from your
boots | b. | feeling as though you're being rocked from side-to-side on a roller
coaster | c. | an apple hanging motionless from the limb of a tree | d. | feeling as though
your head jerks backward when pulling away at green light | e. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
14.
|
Two identical arrows, A and B, are fired with different bows. The bow that fires
arrow A exerts twice the average force as the bow that fires arrow B. Compare the accelerations of
the two arrows.
a. | Arrow B will have twice the acceleration of arrow A. | b. | Arrow A will have
twice the acceleration of arrow B. | c. | Arrow A and arrow B will have the same
acceleration. | d. | Arrow B will have four times the acceleration of arrow A. | e. | Arrow A will have
four times the acceleration of arrow B. |
|
|
|
15.
|
A heavy crate is pushed across a rough surface. The force that is ultimately
responsible for the crate's motion is the
a. | applied force | d. | net force | b. | frictional force | e. | normal force | c. | gravitational
force |
|
|
|
16.
|
A rocket accelerates upward and the thrust of the engines overcome the
frictional forces and the gravity acting against the rocket. Which of Newton's laws of motion
best explains this situation?
a. | Newton's first law | b. | Newton's second law | c. | Newton's third
law | d. | Newton's law of universal gravitation | e. | All the laws combine
to explain this situation. |
|
|
|
17.
|
When analyzing dynamics problems, free-body diagrams
a. | should always be used | b. | are more useful when analyzing horizontal
forces than when analyzing vertical forces | c. | should include only the forces that are
directly responsible for the acceleration | d. | should be used only when objects are
accelerating | e. | only apply to objects in equilibrium |
|
|
|
18.
|
A 24-kg traffic light is suspended from the midpoint of a cable suspended
between two poles. The angle between the cable and the pole is 80° at both poles. The net force acting on the traffic light has a
value of
a. | zero | d. | 2.4 ´ 102 N | b. | 47
N | e. | 4.6 ´ 102 N | c. | 82 N |
|
|
|
19.
|
An object is pushed horizontally at a constant velocity. What can correctly be
said about the forces acting on the object?
a. | The force(s) acting forward is/are greater than the force(s) acting
backward. | b. | The sum of all forces has a value directed forward. | c. | The sum of all
forces is zero. | d. | The forces acting on the object can be said to be
“unbalanced.” | e. | Newton’s second law best summarizes the
effect of the forces acting on the object. |
|
|
|
20.
|
Two masses, A and B, hang on opposite ends of a rope suspended over a pulley.
The mass of A is greater than the mass of B. If 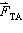 represents the force of tension exerted
by the rope on mass A and 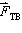 represents the force of tension exerted by the rope on mass
B, then which of the following statements concerning the forces of tension is true?
|
|
|
21.
|
A 1.5-kg cart is pulled with a force of 7.3 N at an angle of 40° above the horizontal. If a kinetic friction force of 3.2 N acts against
the motion, the cart’s acceleration along the horizontal surface will be
a. | 5.0 m/s2 | d. | 1.6 m/s2 | b. | 2.7 m/s2 | e. | 1.0 m/s2 | c. | 2.4
m/s2 |
|
|
|
22.
|
Three masses are suspended vertically as shown in the diagram below. The system
is accelerating upward. What is the relationship among the forces of tension? 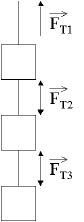
|
|
|
23.
|
Which of the following would be considered an “inertial” frame of
reference?
a. | a moving escalator | b. | a car moving through a turn at a constant
speed | c. | an object in “free fall” | d. | a car pulling away as a traffic light turns
green | e. | all of the above |
|
|
|
24.
|
A 1.4-kg object is pulled horizontally along the floor against 3.2 N of kinetic
friction. If the object accelerates at 5.8 m/s2, what is the value of the applied
force?
a. | 26 N | d. | 6.4 N | b. | 11 N | e. | 4.9 N | c. | 10
N |
|
|
|
25.
|
Which of the following graphs best depicts the relationship between the
gravitational force, F, that two masses exert on one another and the distance, d, which
separates their centres of mass? 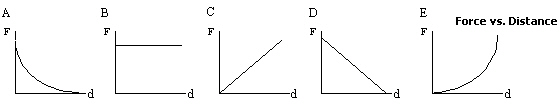
|
|
|
26.
|
According to Newton's law of universal gravitation, the gravitational force
of attraction between two objects would be
a. | half as strong if they're moved twice as far apart | b. | twice as strong if
they're moved half as far apart | c. | four times as strong if they're moved
twice as far apart | d. | four times as strong if they're moved half
as far apart | e. | twice as strong if they're moved twice as far
apart |
|
|
|
27.
|
If Earth was twice its present mass, but its size was not changed, you would
weigh
a. | half as much | d. | one-quarter as much | b. | twice as much | e. | the same amount | c. | four times as
much |
|
|
|
28.
|
What would the gravitational field strength be on a planet with twice
Earth's mass and twice its radius?
a. | 78.4 N/kg | d. | 9.8 N/kg | b. | 39.2 N/kg | e. | 4.9 N/kg | c. | 19.6
N/kg |
|
|
|
29.
|
The coefficient of friction stems from the
a. | nature of the two surfaces in contact | d. | strength of the normal
force | b. | mass of the object | e. | strength of the gravitational force | c. | strength of the applied
force |
|
|
|
30.
|
If all other forces can be ignored and the strength of the frictional force is
greater than the applied force and oppositely directed, the object
a. | could be speeding up or slowing down | b. | must be speeding up | c. | must be slowing
down | d. | could be moving with uniform motion | e. | could be
stopped |
|
|
|
31.
|
For an object travelling with “uniform circular motion,”
a. | its velocity is constant | b. | its acceleration is always directed tangent to
the circle | c. | its velocity is always directed toward the centre of the circle | d. | its speed and
distance from the centre of the circle are constant | e. | its speed may change provided the radius of the
circle is constant |
|
|
|
32.
|
A passenger on a Ferris wheel of diameter 22 m makes one complete revolution
every 45 s. What is the passenger’s centripetal acceleration?
a. | 19 m/s2 | d. | 0.21 m/s2 | b. | 13 m/s2 | e. | 0.068 m/s2 | c. | 0.43
m/s2 |
|
|
|
33.
|
The reason that curves on roads are often banked is because
a. | the coefficient of static friction is increased | b. | the coefficient of
kinetic friction is increased | c. | a component of the normal force can contribute
to the centripetal force | d. | the gravitational force acting on the car is
reduced | e. | the normal force acting on the car is reduced |
|
|
|
34.
|
Imagine you are a passenger upside-down at the top of a vertical looping roller
coaster. The centripetal force acting on you at this position
a. | is perhaps the least of anywhere in the loop | b. | is supplied at least
partly by gravity | c. | is supplied partly by the seat of the roller
coaster | d. | is directed vertically downward | e. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
35.
|
Planet X has a radius 4 times that of Earth and the acceleration due to gravity
at the surface of planet X is 4.9 m/s2. The mass of Planet X compared to Earth’s
mass is
a. | 16 times | d. | 2 times | b. | 8 times | e. | the same | c. | 4
times |
|
|
|
36.
|
To produce an artificial gravity on board a space station
a. | would be impossible | b. | would require an enormous quantity of
matter | c. | is easily achieved by rotating the space station | d. | would be possible by
maintaining an inertial frame of reference | e. | is purely science
fiction |
|
Matching
|
|
|
Match each type of force with its description. a. | normal force | c. | frictional force | b. | gravitational force | d. | net force |
|
|
|
37.
|
This force is always perpendicular to the supporting surface.
|
|
|
38.
|
This force results from cohesive forces among particles in close
proximity.
|
|
|
39.
|
This force is ultimately responsible for the object's
acceleration.
|
|
|
40.
|
This force is exerted by all masses.
|
|
|
Match each of Newton's laws to the situation which they best
describe. a. | Newton's first law | c. | Newton's third
law | b. | Newton's second law | d. | Law of universal gravitation |
|
|
|
41.
|
The force that the Earth exerts on a group of astronauts gets progressively
weaker as their rocket rises vertically upward.
|
|
|
42.
|
At all times the astronauts exert as much force on the Earth as the Earth
exerts on them.
|
|
|
43.
|
The rocket accelerates upward and the engines' combined thrust overcomes
gravity.
|
|
|
44.
|
Astronauts feel as though they're being pushed back into their seats
during launch.
|
|
|
Match the situations described below with the Newton’s law that best
accounts for the motion. a. | Astronauts feel pushed back into their seats during
launch. | b. | The force an astronaut exerts on his seat is equal in strength and opposite in
direction to the force the seat exerts on the astronaut. | c. | The force exerted by
the rocket engine overcomes the forces of gravity and air resistance, resulting in an upward
acceleration of the rocket. |
|
|
|
45.
|
Newton’s first law
|
|
|
46.
|
Newton’s second law
|
|
|
47.
|
Newton’s third law
|
|
|
Study the system diagram below and match the force with the magnitude of its
value. Assume the object is sliding.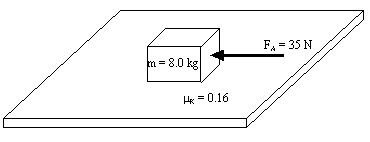
|
|
|
48.
|
gravitational force
|
|
|
49.
|
frictional force
|
|
|
50.
|
net force
|
|
|
The diagram below shows an object travelling with uniform circular motion as
viewed from above. Match each of the following quantities with its proper direction.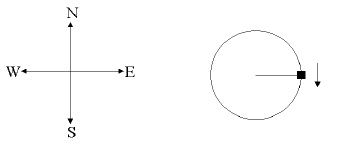 a. | north | c. | east | b. | south
| d. | west |
|
|
|
51.
|
instantaneous velocity
|
|
|
52.
|
centripetal acceleration
|
|
|
53.
|
centripetal force
|
|
|
54.
|
centrifugal force
|
|
|
Match each of the following situations with the type of force responsible for
the object’s centripetal acceleration. a. | gravity | d. | static
friction | b. | tension | e. | kinetic friction | c. | normal |
|
|
|
55.
|
a planet orbiting the Sun
|
|
|
56.
|
a car driving around an icy banked curve
|
|
|
57.
|
a car driving around a flat curve
|