True/False
Indicate whether the
statement is true or false.
|
|
|
1.
|
In a sound wave, the air particles vibrating at the original source move
continually outward towards the listener.
|
|
|
2.
|
In humans with healthy hearing, the audible frequencies range from 20 Hz to 20
000 kHz.
|
|
|
3.
|
Increasing the amplitude of a sound wave also increases the pitch.
|
|
|
4.
|
The observation that beats are produced when two tuning forks of slightly
different frequencies are struck is evidence that sound waves can interfere with one another.
|
|
|
5.
|
As the air temperature decreases, the speed of sound also decreases.
|
|
|
6.
|
In a sound wave, compression is the part of the wave where the particles are
farther apart than normal.
|
|
|
7.
|
Sound is a torsional wave.
|
|
|
8.
|
In general, sound travels most quickly in solids and most slowly in
gases.
|
|
|
9.
|
The base unit for hertz (Hz) is s–1.
|
|
|
10.
|
The nodal point of a standing wave forms due to the continuous destructive
interference of two waves at that point.
|
|
|
11.
|
A suspended pendulum can be forced to move if an identical pendulum is suspended
from the same support due to the effect of sympathetic vibrations.
|
|
|
12.
|
Large buildings, bridges, and other structures can be destroyed by low-speed
winds, sometimes as low as 40 km/h, if they are not properly designed.
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
13.
|
The sound produced by a record album is caused by
a. | the needle vibrating in the grooves of the album | b. | vibrations caused
within the turntable | c. | the stereo amplifier | d. | sound stored on the
vinyl disk | e. | none of the above |
|
|
|
14.
|
Which of the following frequencies is infrasonic?
a. | 12 Hz | d. | 5000 Hz | b. | 25 Hz | e. | 25 000 Hz | c. | 332
Hz |
|
|
|
15.
|
Pitch is not dependent on which of the following wave characteristics?
a. | frequency | d. | amplitude | b. | tone | e. | all of the above | c. | cycles per
second |
|
|
|
16.
|
Which of the following intensities is 100 times greater than 10 dB?
a. | –90 dB | d. | 110 dB | b. | 0 dB | e. | 1000 dB | c. | 30
dB |
|
|
|
17.
|
The frequency of a sound wave is 50 Hz. What is its period?
a. | 0.20 s | d. | 0.020 m/s | b. | 0.020 s | e. | 50 s | c. | 0.020
Hz |
|
|
|
18.
|
An observer is moving away from a stationary ambulance. According to the Doppler
effect, for the observer, the apparent frequency of the siren compared to the actual frequency of the
siren
a. | increases | b. | stays the same | c. | decreases | d. | resonates | e. | increases or
decreases depending on the speed of the ambulance |
|
|
|
19.
|
The intensity level of sound does not depend on which of the following?
a. | amplitude of the vibrating source | d. | frequency of the
source | b. | vibrational energy of the source | e. | none of the above | c. | distance from the
source |
|
|
|
20.
|
What is the main function of the outer ear?
a. | collect the sound from the environment | b. | convert the signal to mechanical
vibrations | c. | convert the signal to neural impulses | d. | transmit and amplify the
sound | e. | maintain balance and orientation |
|
|
|
21.
|
The structure inside the ear that converts mechanical vibrations of sound into
electrical impulses is called the
a. | eardrum | d. | Eustachian tube | b. | cochlea | e. | semicircular canals | c. | oval
window |
|
|
|
22.
|
Sound cannot propagate in which of the following?
a. | solidified air | d. | ice | b. | water vapour | e. | perfect vacuum | c. | water |
|
|
|
23.
|
A marine biologist sends a signal into a lake from the surface. The sound
strikes a school of fish and the echo returns to the biologist 0.020 s after the original signal is
sent. If the speed of sound in water at the time was 1500 m/s, then the depth at which the fish are
located is approximately
a. | 75 km | d. | 15 m | b. | 150 km | e. | 150 m | c. | 30
m |
|
|
|
24.
|
A 256-Hz tuning fork creates sound which travels through the air at 344 m/s. The
distance between adjacent rarefactions is
a. | 67.2 cm | d. | 1.34 m | b. | 2.69 m | e. | 88.0 m | c. | 88.0
cm |
|
|
|
25.
|
Which wave property most affects the intensity or loudness of sound?
a. | reflection | d. | amplitude | b. | complexity | e. | speed | c. | frequency |
|
|
|
26.
|
At normal pressure, what is the speed of sound in air at 0°C?
a. | 0 m/s | d. | 332 m/s | b. | 300 m/s | e. | 344 m/s | c. | 322
m/s |
|
|
|
27.
|
Which of the following frequencies is ultrasonic?
a. | 12 Hz | d. | 5000 Hz | b. | 25 Hz | e. | 25 000 Hz | c. | 332
Hz |
|
|
|
28.
|
The speed of a sound wave as it propagates through air is dependent mainly on
the
a. | period | d. | amplitude | b. | temperature | e. | wavelength | c. | frequency |
|
|
|
29.
|
During destructive interference in sound, which of the following could be
produced?
a. | louder sound | d. | resonance | b. | antinode | e. | supercrest | c. | quieter
sound |
|
|
|
30.
|
The change in direction of a sound wave around corners is called
a. | diffraction | d. | interference | b. | refraction | e. | resonance | c. | reflection |
|
|
|
31.
|
The phenomenon of waves spreading out or bending around the edges of barriers
and openings is called
a. | refraction | d. | interference | b. | diffraction | e. | resonance | c. | reflection |
|
|
|
32.
|
Which property of waves do echoes demonstrate?
a. | diffraction | d. | resonance | b. | interference | e. | reflection | c. | refraction |
|
|
|
33.
|
An ambulance is approaching a stationary observer. For the observer, the
apparent frequency of the siren compared to the actual frequency of the siren
a. | increases or decreases depending on the speed of the ambulance | b. | resonates | c. | decreases | d. | stays the
same | e. | increases |
|
|
|
34.
|
On which of the following is pitch most dependent?
a. | intensity | d. | frequency | b. | amplitude | e. | all of the above | c. | loudness |
|
|
|
35.
|
One sound source has an intensity of 40 dB, while another has an intensity of 70
dB. The intensity of these two differs by a factor of
a. | 3 | d. | 2800 | b. | 30 | e. | 1030 | c. | 1000 |
|
|
|
36.
|
During constructive interference in sound, which of the following could be
produced?
a. | louder sound | d. | resonance | b. | node | e. | supercrest | c. | quieter
sound |
|
|
|
37.
|
Mach number represents
a. | the intensity level of a sound measured in decibels | b. | the speed of sound
at a given temperature | c. | the ratio of an object's speed to the
speed of sound in air at that location | d. | the highest sound frequency that a person can
hear | e. | the lowest sound frequency that a person can hear |
|
|
|
38.
|
You would like two different sound waves to produce audible beats. To do this,
it is necessary that the two sound waves have
a. | exactly the same amplitude and phase | b. | exactly the same amplitude and
frequency | c. | a different number of overtones, or harmonics | d. | amplitudes that are
slightly different | e. | frequencies that are slightly
different |
|
|
|
39.
|
The speed of sound is most dependent on which of the following?
a. | intensity of the sound wave | b. | distance between the source and the
observer | c. | medium in which the sound wave is travelling | d. | frequency of the
original source of the sound | e. | number of crests and troughs in the
wave |
|
|
|
40.
|
What will occur when the two pulses, shown below, interfere with each
other? 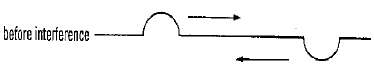 a. | A node is created, then the pulses will continue to travel on
unaffected. | b. | A super crest is created, then the pulses will continue to travel on
unaffected. | c. | A node is created, then the pulses bounce off each other and return to their starting
points. | d. | The two pulses completely destroy each other and they disappear. | e. | The two pulses join
to form a new crest and travel to the left together. |
|
|
|
41.
|
An acoustic guitar contains a sound box that increases the loudness of the
sounds the strings make. This is due to the property called
a. | amplification | d. | resonance | b. | refraction | e. | interference | c. | reflection |
|
|
|
42.
|
A standing wave with three loops is generated in a string. If the wavelength is
10 cm, how far apart are the nodes created?
a. | 2.5 cm | d. | 20 cm | b. | 5.0 cm | e. | 30 cm | c. | 10
cm |
|
|
|
43.
|
A three-loop standing wave is generated in a string by attaching one end to a
wall and letting the transmitted and reflected waves interfere. If the wavelength of the wave is 15
cm, how far from the wall is the first antinode created?
a. | 3.75 cm | d. | 30 cm | b. | 7.5 cm | e. | 45 cm | c. | 15
cm |
|
|
|
44.
|
What is the wavelength of the standing wave shown below? 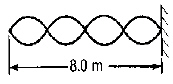 a. | 16 m | d. | 2.0 m | b. | 8.0 m | e. | 1.0 m | c. | 4.0
m |
|
|
|
45.
|
A standing wave with a fundamental mode wavelength of 60 cm forms in an air
column open at both ends. How long is the column for the fundamental mode?
a. | 15 cm | d. | 60 cm | b. | 30 cm | e. | 90 cm | c. | 45
cm |
|
|
|
46.
|
A standing wave with a fundamental mode wavelength of 60 cm forms in an air
column closed at one end. How long is the column for the fundamental mode?
a. | 15 cm | d. | 60 cm | b. | 30 cm | e. | 90 cm | c. | 45
cm |
|
|
|
47.
|
An air column closed at one end is vibrating in its third resonant length. If
the wavelength of the sound is 80 cm, the length of the air column is
a. | 100 m | d. | 1 m | b. | 1 cm | e. | 1.2 m | c. | 120
cm |
|
|
|
48.
|
The first and second resonant lengths of an air column that is closed at one end
are 15.5 cm and 45.5 cm, respectively. The best value for the wavelength of the wave is
a. | 30 cm | d. | 62 cm | b. | 31 cm | e. | 91 cm | c. | 60
cm |
|
Matching
|
|
|
Match the following words to the most appropriate statement below. Note that
not all words will be matched. a. | ultrasonic | g. | eardrum | b. | infrasonic | h. | stirrup | c. | supersonic | i. | cochlea | d. | pitch | j. | auditory nerve | e. | loudness | k. | Eustachian tube | f. | decibel | l. | semicircular canals |
|
|
|
49.
|
term used to describe the frequency or tone of sound
|
|
|
50.
|
frequencies above 20 kHz
|
|
|
51.
|
speeds that are greater than the speed of sound for the given
conditions
|
|
|
52.
|
logarithmic scale used to measure the intensity of sound
|
|
|
Match the following words to the most appropriate statement below. Note that
not all words will be matched. a. | cycle | h. | transverse
vibration | b. | antinodal point | i. | diffraction | c. | refraction | j. | fixed-end reflection | d. | longitudinal
vibration | k. | supercrest | e. | crest | l. | free-end reflection | f. | rarefaction | m. | torsional vibration | g. | nodal point |
|
|
|
53.
|
occurs when an object vibrates perpendicularly to its axis
|
|
|
54.
|
point of destructive interference that remains at rest
|
|
|
55.
|
region in a longitudinal wave where particles are farther apart than
normal
|
|
|
56.
|
bending of a wave due to changing speeds (or mediums)
|
|
|
57.
|
occurs when an object twists around its axis
|
|
|
58.
|
reflection from a rigid end in which the pulse is inverted
|
|
|
59.
|
one complete vibration, oscillation, or back and forth motion
|
|
|
60.
|
interference that results when crest meets crest
|