True/False
Indicate whether the
statement is true or false.
|
|
|
1.
|
Thermal energy refers to the energy possessed by charged particles.
|
|
|
2.
|
When sulfur reacts with oxygen, sulfur dioxide is formed. This is an example of
chemical potential energy.
|
|
|
3.
|
Gravitational potential energy is always measured in relation to an
object's position above the Earth.
|
|
|
4.
|
The energy of a moving object is called kinetic energy.
|
|
|
5.
|
Work is done when a net force is applied to an object over a certain
distance.
|
|
|
6.
|
The unit of work is the joule.
|
|
|
7.
|
To compare the kinetic energy of two objects moving horizontally, you only need
to know the work required to stop each object.
|
|
|
8.
|
When energy changes from one form to another absolutely no energy is
lost.
|
|
|
9.
|
Two substances with the same temperature must have the same thermal
energy.
|
|
|
10.
|
Temperature is the total kinetic energy and potential energy of the atoms or
molecules of a substance.
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
11.
|
A bungee jumper is about to jump from a bridge and he hopes the elastic tied to
his legs will not break as he plummets downward. The type of energy at work when he is at the lowest
point in his downward drop is
a. | gravitational potential | d. | elastic
potential | b. | kinetic | e. | sound | c. | thermal |
|
|
|
12.
|
A solar collector heats the water in the water tank of a home. Which energy
transformation equation best describes this situation?
a. | radiant ® thermal | d. | radiant ® gravitational ®
thermal | b. | radiant ® electrical | e. | radiant ®
thermal ® electrical | c. | radiant ®
gravitational ® electrical |
|
|
|
13.
|
The amount of work done when a 80.00-kg person jumps 1.000 m into the air in
0.5000 s is
a. | 292.0 J | d. | 1568 J | b. | 40.00 J | e. | 160.0 J | c. | 784.00
J |
|
|
|
14.
|
The amount of work done to stop a bullet travelling through a tree trunk a
distance of 50 cm with a force of 2.00 ´ 102 N is
a. | –4.00 ´ 102 J | d. | –1.00 ´ 102 J | b. | +4.00 ´
102 J | e. | +1.00
´ 104 J | c. | +1.00 ´
102 J |
|
|
|
15.
|
A 55-kg person is skating on the Rideau Canal. She reaches a maximum speed and
then glides to a stop in 100 m. The coefficient of friction between her skates and the ice is 0.010.
What is the work done by the kinetic friction?
a. | –5.5 ´ 101 J | d. | –5.5 ´ 105 J | b. | –5.4 ´
102 J | e. | +5.4 ´ 102 J | c. | +5.5 ´
101 J |
|
|
|
16.
|
Armen records the amount of force he applies to his toboggan each metre as it is
pulled on a level, frictionless surface. The data is listed in the table below. How much work did
Armen do on the toboggan? Force (N) | Distance (m) | 2.0 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 | | |
a. | +2.0 J | d. | –8.0 J | b. | –2.0 J | e. | +20 J | c. | +8.0
J |
|
|
|
17.
|
Calculate the work done by planet X on its moon. Planet X applies a force of 5.6
´ 1010 N on its moon and the moon is 4.0 ´ 108 km away from the planet and it continues to circle the
planet in a circular orbit of circumference of 2.5 ´ 109
m.
a. | 0.0 J | d. | +2.2 ´ 1019
J | b. | –2.2 ´ 1019 J | e. | –1.4 ´
1020 J | c. | +1.4 ´
1020 J |
|
|
|
18.
|
The unit of work is the joule (J) which is equivalent to
a. | kg·m/s2 | d. | watt | b. | kg·m3/s2 | e. | kg·m2/s2 | c. | kg·m/s |
|
|
|
19.
|
In which case is negative work done?
a. | The work done by Earth on a ball as the ball, which was initially at rest, falls 3.0
m down towards Earth. | b. | A eastward force is applied to an eastward
moving soccer ball that is already moving at a constant velocity to increase its speed in that
direction. | c. | A cart is moving at a constant velocity of 10 m/s [W] when a 0.5 N
[downward] force is applied. | d. | The work done by Earth on an arrow as it is
fired 200 m straight up into the air. | e. | Earth applies a force on the Moon as the Moon
travels one completion rotation in orbit around Earth. |
|
|
|
20.
|
In which case is positive work done?
a. | The work done by air resistance on a ball as the ball, which was initially at rest,
falls 3.0 m down towards Earth. | b. | A eastward force is applied to an eastward
moving soccer ball that is already moving at a constant velocity to increase its speed in that
direction. | c. | Earth applies a force on the Moon as the Moon travels one completion rotation in
orbit around Earth. | d. | A cart is moving at a constant velocity of 10
m/s [W] when a 0.5 N [downward] force is applied. | e. | The work done by
Earth on an arrow as it is fired 200 m straight up into the air. |
|
|
|
21.
|
In which case is positive work done?
a. | A eastward force is applied to an eastward moving soccer ball that is already moving
at a constant velocity to increase its speed in that direction. | b. | A cart is moving at
a constant velocity of 10 m/s [W] when a 0.5 N [E] force is
applied. | c. | Earth applies a force on the Moon as the Moon travels one completion rotation in
orbit around Earth. | d. | The work done by air resistance as a baseball
is thrown horizontally towards the catcher. | e. | The work done by air resistance on a ball as
the ball, which was initially at rest, falls 3.0 m down towards
Earth. |
|
|
|
22.
|
The motion of a skateboard is shown on the velocity-time graph below. 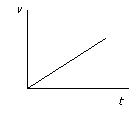 Which one of the following kinetic energy-time graphs best represents the motion of
the skateboard?
|
|
|
23.
|
The motion of a skateboard is shown on the acceleration-time graph
below. 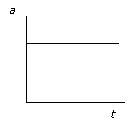 Which one of the following kinetic energy-time graphs
best represents the motion of the skateboard?
|
|
|
24.
|
A 5.00-kg sack of potatoes is raised to a height of 2.00 m and then thrown at a
constant velocity of 2.00 m/s onto a truck. What is the kinetic energy of the potatoes?
a. | 5.00 J | d. | 103 J | b. | 98.0 J | e. | 108 J | c. | 10.0
J |
|
|
|
25.
|
A 100-g Frisbee is thrown at a speed of 5.5 m/s, 1.3 m above the ground. The
Frisbee has a potential energy of
a. | 1.3 ´ 105 J | d. | 1.5 ´ 100 J | b. | 2.8 ´
100 J | e. | 2.8 ´ 105 J | c. | 1.3 ´
100 J |
|
|
|
26.
|
In the following figure, a 0.60-kg ball is about to fall to the step
below. 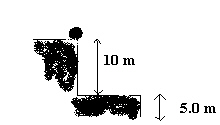 The gravitational potential energy of the ball relative
to the step is a. | 8.8 ´ 101 J | d. | 3.0 ´ 100 J | b. | 2.9 ´
101 J | e. | 5.9 ´ 101 J | c. | 6.0 ´
100 J |
|
|
|
27.
|
A box of mass m slides down a ramp of length l. The ramp has a
vertical height h. The change in the gravitational potential energy is
|
|
|
28.
|
A roller coaster has two vertical loops one after the other. The roller coaster
has a speed of 7.00 m/s at the top of the first loop with a height of 22.2 m. It then proceeds around
the second vertical loop with a height of 15.0 m. What is the speed of the roller coaster at the top
of the second vertical loop?
a. | 7.00 m/s | d. | 9.24 m/s | b. | 13.8 m/s | e. | 11.2 m/s | c. | 8.40
m/s |
|
|
|
29.
|
Two girls are playing baseball in a park. The batter hits the 400-g ball with a
speed of 20.0 m/s. It travels over the park's fence that is 4.00 m high. Assuming that the ball
loses half of its energy to air resistance, at what speed does the ball travel over the fence?
a. | 5.00 m/s | d. | 17.9 m/s | b. | 10.0 m/s | e. | 14.1 m/s | c. | 7.37
m/s |
|
|
|
30.
|
A pendulum bob is released from rest at a height of 1.50 m and the following
data was collected for each cycle.Assume the lowest point is 0 m. Maximum height of bob (m) | Maximum speed of bob at lowest
point | 1.50 | 5.42 | 1.50 | 5.42 | 1.50 | 5.42 | 1.50 | 5.42 | | |
Which statement most accurately describes the
experiment? a. | The data shows that the experiment was not a controlled one. | b. | The experiment shows
that energy was conserved. | c. | It is not possible to relate the energies
without the mass of the bob. | d. | The data shows that the gravitational potential
energy decreased while the kinetic energy increased. | e. | The experiment shows no relationship between
gravitational potential and kinetic energy. |
|
|
|
31.
|
How much heat is required to raise the temperature of 40 g of water
20°C?
(cw = 4.18 ´ 103
J/kg·°C)
a. | 5.2 J | d. | 3.3 ´ 105
J | b. | 3.3 ´ 103 J | e. | 2.1 ´
106 J | c. | 8.0 ´ 10–1
J |
|
|
|
32.
|
Specific heat capacity is the quantity of heat
a. | required to change 1 kg of a substance from a liquid to a gas | b. | given off by a 1-kg
substance that changes state from solid to liquid | c. | required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of a
substance from 1°C to 100°C | d. | needed to melt 1 kg of a substance without a
change in temperature | e. | required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of a
substance 1°C |
|
|
|
33.
|
The specific heat capacity of iron is 4.5 ´
102 J/kg·°C. The heat energy required to heat 5.0 kg
of iron from 10°C to 40°C is
a. | 9.0 ´ 104 J | d. | 2.2 ´ 104 J | b. | 6.8 ´
104 J | e. | 7.5 ´ 101 J | c. | 3.0 ´
100 J |
|
|
|
34.
|
A liquid is being heated on a hotplate. The transfer of heat in the liquid
through a circular path is called
a. | radiation | d. | conduction | b. | convection | e. | heat exchange | c. | heat
transfer |
|
|
|
35.
|
The process by which energy is transferred by means of electromagnetic waves
is
a. | radiation | d. | conduction | b. | convection | e. | heat transfer | c. | heat
exchange |
|
|
|
36.
|
A 40.0-kg boy rides his 0.70-kg skateboard. He starts at 1.0 m/s and at a
constant acceleration reaches 3.0 m/s in 10 s on a horizontal surface. How much power did he
use?
a. | 1.6 ´ 101 W | d. | 8.1 ´ 102 W | b. | 4.1 ´
100 W | e. | 6.1 ´ 100 W | c. | 1.8 ´
101 W |
|
Matching
|
|
|
Match each item with the its correct unit below. (Use each item only
once.) a. | power | d. | temperature | b. | work | e. | specific heat capacity | c. | efficiency | f. | energy |
|
|
|
37.
|
joule per kilogram×degrees Celsius
(J/kg·ºC)
|
|
|
38.
|
joule (J)
|
|
|
39.
|
percentage
|
|
|
40.
|
newton metre (N·m)
|
|
|
41.
|
watt (W)
|
|
|
42.
|
degrees Celsius (ºC)
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct answer below. a. | principle of heat exchange | g. | thermal energy | b. | radiation | h. | conduction | c. | temperature | i. | kinetic | d. | convection | j. | nuclear potential | e. | electrical | k. | specific heat capacity | f. | gravitational
potential | l. | elastic
potential |
|
|
|
43.
|
Amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1.0 kg of a substance by
1.0°C.
|
|
|
44.
|
Process where heat is transferred by collision of atoms.
|
|
|
45.
|
The energy stored in an elastic band when it is stretched.
|
|
|
46.
|
Energy that can be transferred through a vacuum.
|
|
|
47.
|
A soccer ball is kicked towards a net. As it travels through the air it
possesses this type of energy.
|
|
|
48.
|
Total kinetic and potential energy of the particles in a substance.
|
|
|
49.
|
Amount of heat lost by a hot body is the amount of heat gained by cold
body.
|
|
|
50.
|
You would use this energy to run your portable tape player.
|
|
|
51.
|
Average kinetic energy of particles of a substance.
|
|
|
52.
|
A hammer held above a nail at a height of 3 cm possesses this type of
energy.
|
|
|
53.
|
Process where heat is transferred by a circulating path.
|
|
|
54.
|
Uranium-235 atoms release this type of energy when split open.
|