True/False
Indicate whether the
statement is true or false.
|
|
|
1.
|
A conductor does not transfer electrons very well.
|
|
|
2.
|
The electric force between two charged objects decreases as they get closer to
each other.
|
|
|
3.
|
Electric field lines travel away from a positive charge and towards a negative
charge.
|
|
|
4.
|
A direct current always flows in the same direction in a circuit.
|
|
|
5.
|
A compass can be used to detect the direction of a magnetic field.
|
|
|
6.
|
The magnetic field of a bar magnet is weakest at its poles.
|
|
|
7.
|
If the direction of the current in a coil is reversed, the poles of the magnetic
field in the coil will also be reversed.
|
|
|
8.
|
The magnetic field of a conductor is made weaker when it is twisted into a
loop.
|
|
|
9.
|
The strength of an electromagnet may be increased by decreasing the current in
the conductor.
|
|
|
10.
|
Removing some coils from an electromagnet will make the magnet stronger.
|
|
|
11.
|
When using the right hand rule for the motor principle, your thumb represents
the direction of the force on the conductor.
|
|
|
12.
|
A motor converts electrical energy to kinetic energy.
|
|
|
13.
|
A current is produced in a conductor when a magnetic field is moved around it,
but not when the conductor is moved through a magnetic field.
|
|
|
14.
|
When a bar magnet is plunged into a coil, a current is induced in the
coil.
|
|
|
15.
|
In electromagnetic induction, the induced field opposes the inducing
field.
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
16.
|
An electrically neutral pith ball gains 4.0 ´
1023 electrons. Its charge is now
a. | –2.5 ´ 104 C | d. | –4.0 ´ 1023 C | b. | +1.6 ´
10–19 C | e. | –1.4 ´ 10–18
C | c. | –6.4 ´ 10 4
C |
|
|
|
17.
|
The SI unit for measuring charge is the
a. | coulomb | d. | joule | b. | ampere | e. | watt | c. | volt |
|
|
|
18.
|
A circuit has a current of 345 mA. How much charge passes a point in the circuit
in 2.00 min?
a. | 0.690 A | d. | 20.7 A | b. | 2.88 A | e. | 41.4 A | c. | 5.75
A |
|
|
|
19.
|
How many seconds will it take for 10.0 C of charge to pass through a 12.0 A
circuit?
a. | 120 s | d. | 100 s | b. | 0.120 s | e. | 1.20 s | c. | 0.833
s |
|
|
|
20.
|
In what type of circuit do electrons follow one path from the source, to a load,
and back to the source?
a. | short circuit | d. | series circuit | b. | open circuit | e. | connected circuit | c. | parallel
circuit |
|
|
|
21.
|
The value of V2 in the following circuit is 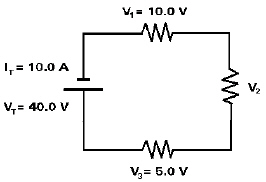 a. | 40 V | d. | 15 V | b. | 35 V | e. | 10 V | c. | 25
V |
|
|
|
22.
|
A circuit has a 120-V source. If the current is 10.0 A, the resistance in the
circuit must be
a. | 10.0 W | d. | 1.20 ´ 102 W | b. | 8.33 ´ 10–2 W | e. | 12.0 W | c. | 1.20 ´ 103
W |
|
|
|
23.
|
The units used to measure charge, current, potential difference, and resistance
are, respectively,
a. | ampere, joule, ohm, volt | d. | ampere, joule, volt,
ohm | b. | coulomb, ampere, volt, ohm | e. | ampere, coulomb, ohm, volt | c. | coulomb, ampere, ohm,
watt |
|
|
|
24.
|
Which combination of resistors will produce the lowest total resistance in a
circuit?
a. | two 10-W resistors in series | d. | three 10-W resistors in parallel | b. | two 10-W resistors
in parallel | e. | four 10-W resistor in series | c. | three 10-W resistors
in series |
|
|
|
25.
|
A toy train set runs on a current of 250 mA. It has a resistance of 20 W. If the train ran for 60 min, how much energy was did the train use?
a. | 5.0 J | d. | 4.5 ´ 103
J | b. | 12 J | e. | 5.0
´ 102 J | c. | 75 J |
|
|
|
26.
|
A 9.0-V battery produces a current of 8.0 A. What is the resistance in the
circuit?
a. | 1.1 W | d. | 5.3 W | b. | 0.89 W | e. | 72
W | c. | 0.75 W |
|
|
|
27.
|
A toy train set has a resistance of 20.0 W and uses a
current of 250 mA. If it ran for
one hour, what is the power of the train?
a. | 1.2 W | d. | 2.2 ´ 102
W | b. | 5.0 W | e. | 4.5
´ 103 W | c. | 75 W |
|
|
|
28.
|
Three 10.0-W resistors are connected in parallel to
one another in a 12.0-A circuit. The total resistance in the circuit is
a. | 0.0333 W | d. | 20.0 W | b. | 0.300 W | e. | 30.0
W | c. | 3.33 W |
|
|
|
29.
|
A load has a resistance of 20.0 W. If 40.0 C of
charge pass through it in 10.0 s, what is the potential difference of the load?
a. | 5.00 V | d. | 8.00 ´ 102
V | b. | 20.0 V | e. | 8.00
´ 103 V | c. | 80.0 V |
|
|
|
30.
|
Magnetic field lines
a. | show the strength of a magnetic field | b. | show the direction of a magnetic
field | c. | become more widely spaced as the magnetic force weakens | d. | all of the
above | e. | none of the above |
|
|
|
31.
|
The circle between the ends of the horseshoe magnet shown below represents a
compass. If the pole on the left is the N-pole, in which direction will the needle of the compass
point? 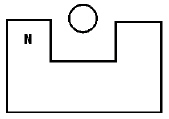 a. | to the left | d. | down | b. | to the right | e. | in circles | c. | up |
|
|
|
32.
|
What will most likely happen when a bar magnet made of iron is heated?
a. | The magnet will be permanent. | b. | The magnet will become
stronger. | c. | The magnet will become weaker. | d. | The poles of the magnet will
reverse. | e. | The magnet will become ferromagnetic. |
|
|
|
33.
|
An iron nail can be turned into a temporary magnet if it is held in a strong
magnetic field. This method of magnetization is called
a. | induction | d. | charging | b. | saturation | e. | convection | c. | conduction |
|
|
|
34.
|
A conductor be attracted by a magnet when
a. | The conductor contains negative electrons. | b. | The conductor
contains positive protons. | c. | The conductor contains moving
electrons. | d. | all of the above | e. | none of the
above |
|
|
|
35.
|
Which of the following factors does not affect the size of the induced current
in a coil?
a. | number of turns in the coil | d. | size of the inducing
field | b. | rate of change of the inducing field | e. | direction of the windings in the
coil | c. | resistance of the wire in the coil |
|
|
|
36.
|
To use the right hand rule to predict the direction of an induced current in a
coil, your thumb must point
a. | To the N-pole of the induced magnetic field. | b. | To the S-pole of the
induced magnetic field. | c. | In the direction of the induced
current. | d. | In the direction of the inducing field. | e. | In the direction of
the electron flow. |
|
|
|
37.
|
Which of these factors would increase the output of a generator?
a. | increasing the rate of rotation of the armature | b. | increasing the
strength of the field magnets | c. | increasing the number of coils on the
armature | d. | all of the above | e. | none of the
above |
|
|
|
38.
|
A step-down transformer changes
a. | High potential difference to low potential difference. | b. | AC current to DC
current. | c. | High current to low current. | d. | High resistance to low
resistance. | e. | DC current to AC current. |
|
Matching
|
|
|
Match each definition with the letter of the correct term. A letter may be
used more than once, or not at all. a. | energy | d. | power | b. | resistance | e. | potential difference | c. | current | f. | work |
|
|
|
39.
|
rate at which charge travels in a circuit
|
|
|
40.
|
amount of work needed to move a unit charge between two points
|
|
|
41.
|
measured in amperes (A)
|
|
|
Match the name of each scientist with the contribution that he made. A letter
may be used more than once, or not at all. a. | Andre Ampere | e. | Charles
Coulomb | b. | Robert Millikan | f. | Gustav Kirchoff | c. | Georg Ohm | g. | James Watt | d. | Benjamin
Franklin | h. | Alessandro
Volta |
|
|
|
42.
|
determined that the size of the force between two charged objects is directly
proportional to the product of the charges
|
|
|
Match each term to the letter of the circuit type it best describes. A letter
may be used more than once, or not at all. a. | short circuit | d. | parallel
circuit | b. | open circuit | e. | closed circuit | c. | series circuit |
|
|
|
43.
|
electrons all travel the same path in the circuit
|
|
|
44.
|
circuit with a break in it
|
|
|
45.
|
electrons can return to a source without passing through a load
|
|
|
46.
|
potential decrease is constant across all loads
|
|
|
Match each term with the letter of the circuit component that it best
describes. A letter may be used more than once, or not at all. a. | battery | d. | ground | b. | light bulb | e. | wire | c. | ammeter | f. | voltmeter |
|
|
|
47.
|
provides a path for electrons to travel
|
|
|
48.
|
removes energy from the circuit
|
|
|
49.
|
removes charge from the circuit
|
|
|
50.
|
classified as a source
|
|
|
Match each quantity with the letter of the device that is most suitable for
measuring it. A letter may be used more than once, or not at all. a. | voltmeter | e. | compass | b. | ammeter | f. | stopwatch | c. | electroscope | g. | meter stick | d. | balance |
|
|
|
51.
|
amount of time a circuit is in operation
|
|
|
52.
|
relative size of an electric charge
|
|
|
Match each definition with the letter of the term it best describes. A letter
may used more than once, or not at all. a. | diamagnetic | d. | paramagnetic | b. | ferromagnetic | e. | nonmagnetic | c. | magnetic |
|
|
|
53.
|
material that can attract small pieces of iron
|
|
|
54.
|
material that cannot become a magnet
|
|
|
55.
|
nickel is an example of this kind of material
|
|
|
Match each item with the letter of the term it best describes. A letter may
used more than once, or not at all. a. | brush | d. | armature | b. | split-ring commutator | e. | coil | c. | slip
ring | f. | field
magnet |
|
|
|
56.
|
induces the magnetic field in the coil
|
|
|
57.
|
rotates the coil in the magnetic field
|
|
|
58.
|
provides a constant magnetic field
|