LESSON
06 – IMAGES ON THE WEB
IMAGE SHAPE
Every image is a rectangular arrangement of tiny dots called pixels. Some image may seem to be a different shape
but in reality, they are rectangular with some border pixels being transparent.
|
Example |
|
|
|
Here is an example of an image that seems to be circular. However, this is simply because the outside
part of the image is either transparent or matches the background. |
PIXELS
Each dot in
an image is a pixel. Each pixel has a
specific color. The more pixels in your
image, the larger it will be. This means
it will be of better quality but also a larger file size.
TWO FAMILIES OF IMAGES
A raster image is simply an image that
has a color associated with each pixel.
A vector image is an image
that is stored in terms of shapes (such as lines, dots, triangles, ellipses, …).
|
Rasters |
Vectors |
|
|
|
Example |
|
|
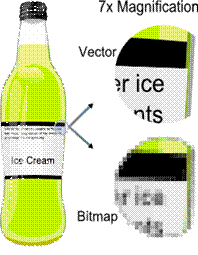
The image
on the right (from Wikipedia) shows the difference between a vector graphic
and a raster graphic (bitmap) when one resizes the image. As you can
see, the vector graphic is far superior and required for company logos to
keep the desired professional look. |
|
Our focus
will be on raster images for now because they are so common.
MEGAPIXELS
We have
already seen that an image is rectangular.
Therefore, it has a width and a height which are both measure in
pixels. We can calculate the total
number of pixels in an image by:
Total pixels = width x height
So, cameras
that are 12 megapixels store about 12 million different little dots for each
picture they take!
FILE SIZE
The more
pixels that are in an image, the larger the image file will be. For web pages, this is an issue because large
images take time to transfer. In fact,
for users that have slow internet connections, large images can slow the
displaying of a website down considerably.
Therefore, it
is a good idea to reduce an image’s size.
To do this, you have to open the image in a graphic editor such as
Paint, Paint.NET or Photoshop, resize it and save it. Changing the image’s width or height in html
does not reduce the image’s file size!
RASTER IMAGE FORMATS
We will learn
more about image formats in the Graphics Unit.
However, it is important to understand that each format is a different
way to store an image. A format is like
a language. If the user or program
doesn’t understand that language, the image cannot be displayed or seen.
HOW TO CHECK AN IMAGE’S
FORMAT
One can tell
the format of an image by checking its file extension. It will be usually either
JPG, BMP, GIF or PNG.
It does
happen that this extension is incorrect (rarely). We will see how to check this later.
CONVERTING IMAGE FORMATS
The easiest
way to convert to an image to a different format is to:
1 – Open the
image in Paint.
2 – Go File
> Save As
3 – At the
bottom near the filename, pick the format you want in the drop down menu.
COMMON ERROR
Do not ever
simply rename the file with a new file extension and hope that will work. It will cause problems in a web browser (even
if everything in Windows seems fine).
CHECKING AN IMAGE’S
FORMAT
It is fairly
common that an image that has an extension is actually stored as a different
type. For example, you might have an
image that is called flower.jpg.
However, it’s in fact a bmp file.
This causes a
problem because Windows is able to deal with this issue and simply displays the
image without pointing out the problem.
However, your web browser is not as smart. It cannot deal with this problem and will not
display your image.
So, if you
need to check to make sure your image’s file extension matches it’s type, you
can do the following:
1 – Make a
mental note of the image’s file extension.
2 – Open the
image in Paint.
3 – Go File
> Save As
4 – If the
File Type at the bottom does not match the file extension, then this is a
problem!