LESSON 05 – COMBINATION CIRCUITS
LESSON NOTE
A
combination circuit is simply a circuit that contains loads in series and in
parallel.
EXAMPLE
1
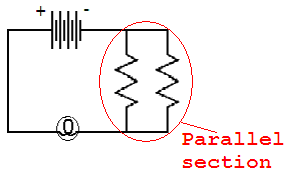
In the
following combination circuit, an electron first goes through one of the
branches in the parallel section and then goes through the light bulb (in
series). If an electron has to go through more than one load, it is going
through a series of loads (series circuit).
EXAMPLE
2
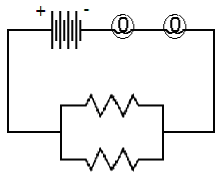
In the
following combination circuit, an electron first goes through two light bulbs
and then through one of the parallel branches.
EXAMPLE
3
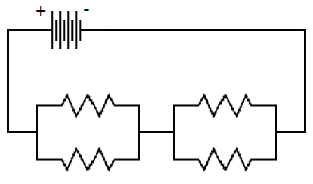
The
following combination circuit consists of two parallel sections that are in
series.
EXAMPLE
4
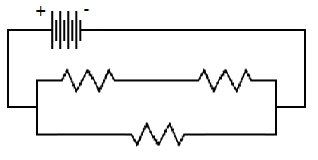
The
following combination circuit consists of a parallel section. One of the branches consists of two loads
in series.
PROPERTIES
OF COMBINATION CIRCUITS
The
properties are simple. Sections that
are in parallel are dealt with using the rules of parallel circuits. Sections that are in series are dealt with
using the rules of series circuits.
SOLVING TECHNIQUES
There are
two approaches to solving such problems.
One approach
is to use the single table like before.
However, the columns in such a table no longer follow strictly series
or parallel rules. You will have to
use analysis to figure values when you are stuck.
Another
approach is to use a multi-table system.
Essentially, you create a different table for each sub-series or
sub-parallel section. This involves a
fair bit of extra writing but allows you to continue solving the tables like
before.
We will look at both approaches
in the examples.
|