|
Java OOP
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS INHERITANCE &
POLYMORPHISM I
SOLUTIONS 1-Inheritance
3-class
hierarchy 4-subclass,
child 5-superclass,
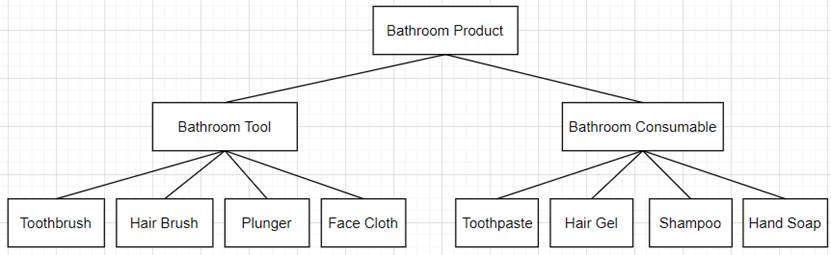
parent 6-extends 7-Tool 8-Foot 9-Diagram:
10b) None of
these items are related to one another.
A Cup is not a Marker or a Shoe or a House. Nothing else is a Cup. We can say the same for all other
classes. So, no this is not a case
where we could use inheritance. 10c) Yes, we
can use inheritance here. Food could
be Fruit’s superclass because Fruit is Food.
Then, Fruit could be the superclass for the other three classes. 10d) No these
are not suitable for inheritence. There is no superclass here. If we wanted to use inheritance, we would
have to add a superclass such as Vegetable or Food. 10e) Not
quite. While Missile can be the
superclass for the next three classes, there is no obvious relationship
between Cannon and Missile (or the other classes). So inheritance could be used for the first
four terms, but not for Cannon. 11-instance
variables, instance methods 12-overriding
method 13-superconstructor,
superclass 14-super 15-See the
addition in blue in the code below.
16-When using
super, the parameters much match the parameter lists of one of the superconstructors.
|
||||||||
|
|