|
Java Swing - Graphics
TOPIC 03 –AFFINE TRANSFORMATIONS

LESSON NOTE

TRANSFORMATIONS
A transformation is simply an altering of an image
or shape. This can happen by rotating,
translating or mirroring. It can also
happy be shearing (stetching).
THE AFFINETRANSFORM CLASS
Java provides the AffineTransform
class that allows you to do transformations on all objects before they are
drawn.
We’ll look at how to do rotation, translation,
shearing and mirroring in the next examples.
ROTATION ANGLE
Before talking about how to do rotation, it is
important to realize that the angle is specified in radians instead of in
degrees. Here’s a chart showing
different common angles in both radians and degrees.
|
Degrees
|
Radians
|
|
360
|
2 * Math.PI
|
|
180
|
Math.PI
|
|
90
|
Math.PI / 2
|
|
60
|
Math.PI / 3
|
|
45
|
Math.PI / 4
|
|
10
|
Math.PI / 18
|
|
Angle a
|
a * Math.PI / 180
|
ROTATION
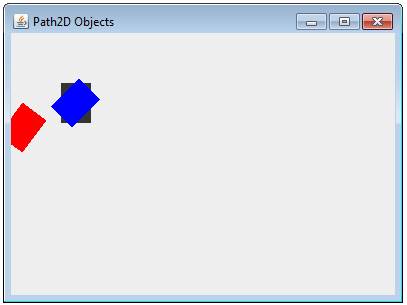
In the code below in the second class, a Rectangle
is being drawn three different times.
The first time, it’s drawn normally without any
transformation.
The second time, a rotation transformation is
applied. The rotation is anchored at
the origin (0,0).
This is the default. So when
the object is drawn (in red), it is rotated 36 degrees in the clockwise
direction.
The third time, a rotation transformation is again
applied. However, this time, the
rotation anchor is set to the center of the rectangle so the rectangle is
drawn (in blue) at the same location but rotated on itself.
|
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class RotationTester
{
public static void
main(String[] args)
{
JFrame jf = new JFrame();
jf.setSize(400,300);
jf.setVisible(true);
jf.setTitle("Path2D
Objects");
//Create my panel and add it to JFrame
object
RotationPanel pan = new RotationPanel();
jf.add(pan);
}
}
|
|
package
Java2DStuff;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import
java.awt.Graphics2D;
import java.awt.Panel;
import java.awt.geom.AffineTransform;
import
java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D;
public class RotationPanel extends Panel
{
public void
paint(Graphics g)
{
Graphics2D g2D = (Graphics2D)g;
//================
//RECTANGLE #1
//================
//Create and fill rectangle.
Rectangle2D.Double r = new
Rectangle2D.Double(50,50,30,40);
g2D.fill(r);
//================
//RECTANGLE #2
//================
//Set colour to red.
g2D.setColor(Color.red);
//Create and apply rotation transformation (centered on
origin)
AffineTransform at = new AffineTransform();
at.setToRotation(Math.PI / 5); //Math.PI is 180 degrees, so 180 / 5 = 36 degrees
g2D.setTransform(at);
//Draw same rectangle object as above.
g2D.fill(r);
//================
//RECTANGLE #3
//================
//Set colour to blue.
g2D.setColor(Color.blue);
//Create a new rotation transformation
//This time, center the rotation at the middle of the
original rectangle (65,70).
AffineTransform at2 = new AffineTransform();
at2.setToRotation(Math.PI / 4, 65, 70); //180 / 4 = 45
degrees
g2D.setTransform(at2);
//Draw same rectangle object as above.
g2D.fill(r);
}
}
|
The code above creates the following:
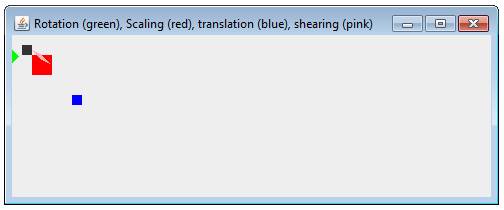
EXAMPLE WITH OTHER TRANSFORMATIONS
The
following example will demonstrate all transformations in a single
program.
|
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class AffineTransformTester
{
public static void
main(String[] args)
{
JFrame jf = new JFrame();
jf.setSize(400,200);
jf.setVisible(true);
jf.setTitle("Rotation
(green), Scaling (red), translation (blue), shearing (pink)");
//Create my
panel and add it to JFrame object
AffineTransformPanel
pan = new AffineTransformPanel();
jf.add(pan);
}
}
|
|
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.Graphics2D;
import java.awt.geom.*;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
public class AffineTransformPanel extends JPanel
{
public void
paint(Graphics g)
{
Graphics2D g2D = (Graphics2D)g;
//Create original
rectangle and fill it in black.
Rectangle2D.Double r1 = new
Rectangle2D.Double(10,10,10,10);
g2D.fill(r1);
//Set color to
blue.
g2D.setColor(Color.blue);
//Create a
TRANSLATION transformation, apply it and display rectangle
AffineTransform
at = new AffineTransform();
at.setToTranslation(50,50); //move over 50 in x direction
and 50 in y direction
g2D.setTransform(at);
g2D.fill(r1);
//Set color to
green.
g2D.setColor(Color.green);
//Create a
ROTATION transformation, apply it and display rectangle.
AffineTransform
at2 = new AffineTransform();
at2.setToRotation(Math.PI / 4); //45 degrees
g2D.setTransform(at2);
g2D.fill(r1);
//Set color to red.
g2D.setColor(Color.red);
//Create a
SCALING transformation, apply it and display rectangle.
AffineTransform
at3 = new AffineTransform();
at3.setToScale(2, 2); //double the scale for both x
and y
g2D.setTransform(at3);
g2D.fill(r1);
//Set color to
pink.
g2D.setColor(Color.pink);
//Create a
SHEARING transformation, apply it and display rectangle.
AffineTransform
at4 = new AffineTransform();
at4.setToShear(1, 0.5); //stretch object in both
directions
g2D.setTransform(at4);
g2D.fill(r1);
}
}
|
The
code above will create:
CUMULATIVE EFFECT
If
you want to apply two or more transformations at once, it’s easy. You simply use the following method calls
instead.
Let’s
assume the AffineTransform object is called at
and we want to translate drawings over to the right by 10 and then rotate them
by 90 degrees. Here’s the code:
at.translate(10,0);
at.rotate(Math.PI/2);

|

