|
Java
Swing - GUIs
LESSON NOTE - JCHECKBOX
JCHECKBOX CONSTRUCTOR We
create a JCheckBox by specifying the text
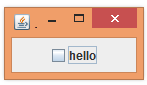
associated with the checkbox. JCheckBox cb = new JCheckBox("hello"); After
adding the JCheckBox to the content pane, we get
this:
SELECTED? To know the state of the
checkbox, we use the isSelected() method.
It returns either true or false. boolean
state = cb.isSelected(); SETTING THE STATE To set the state of the
checkbox to either selected or not selected, we use the setSelected(boolean)
method. cb.setSelected(true); ACTION LISTENER We can add an action
listener to the JCheckBox. After we do
so, an event is triggered whenever the checkbox is clicked on. ACTIONPERFORMED METHOD To
respond to an event, we check the source of the event. If the event comes from the JCheckBox, then we get the selected text or index. public
void actionPerformed(ActionEvent
e) { if (e.getSource() == cb) { System.out.println("Selected? " + cb.isSelected()); } } FULL CODE EXAMPLE Here
is a complete example that shows the concepts from above in action.
|
|
|
|