|
Java TOPIC 14 – IF STATEMENTS I
LESSON NOTE
BOOLEAN VARIABLE A boolean variable is a variable that can have
a value of either true or false.
It only takes up one bit of memory. Like
all other variables, a boolean variable has to be
declared and initialized before being used. EXAMPLE – Declare a boolean
variable named t and initialize it to true. boolean t = true;
BOOLEAN EXPRESSIONS A boolean expression is an expression that
evaluates to a boolean value (true or false). EXAMPLE – Here is a simple boolean expression: t > 4 The
above expression will be true if t is greater than 4 and false otherwise. CONDITIONS Boolean
expressions used inside If statements are referred to as conditions. And if statements
are often called conditional
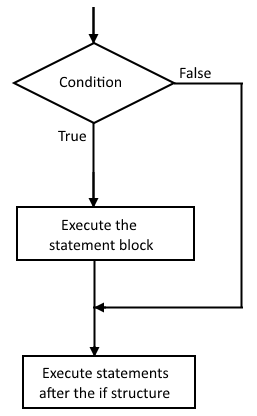
statements. IF STRUCTURE Here
is the structure of a basic if-statement: if (condition) { //statement block to be executed if
condition is true } Whenever
the condition is true, then the statement block inside the {
and } is executed. However,
whenever the condition is false, the entire statement block is skipped. IF STRUCTURE FLOWCHART Below
is a flowchart that shows how an IF statement is executed. EXAMPLE PROGRAM Here
is a program that asks the user for their grade. It outputs a message only if they are
failing. Nothing is done if they are
passing. System.out.println("Enter your grade in this course."); int mark = scr.nextInt(); if (mark < 50) { System.out.println("You are failing."); } CONDITIONAL OPERATORS Here
are Java’s conditional operators:
EXAMPLES – Write the boolean
expression that is true if a)
k
is less than 17 k
< 17 b)
coco
is greater or equal to zero
c)
t
is greater than or equal to the square root of 34 t
>= Math.sqrt(34) d)
c2
is equal to a2 + b2 c * c == a * a + b * b e)
w
is an even number w
% 2 == 0 f)
x
is an odd number x
% 2 == 1 g)
y
is not equal to 4 y
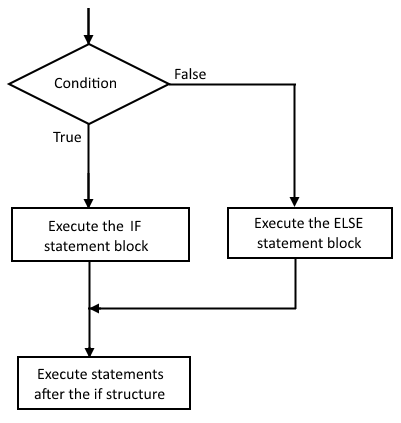
!= 4 IF / ELSE STRUCTURE It
is often useful to also have a statement block that gets executed whenever
the condition in the if statement is false. This can be done by adding an else to the if
structure. if (condition) { //the IF statement block (executed if
condition is true) } else { IF / ELSE STRUCTURE
FLOWCHART VARIABLE SCOPE A
variable that is declared inside a statement block only exists inside that
block. Variables
that are declared before the block can be used inside and after the block. COMPARING STRINGS To
compare Strings, we need to use the .equals method. EXAMPLE The
condition below is true is String s is equal to “James”. if (s.equals("James")) { … } The
condition below is true if Strings word1 and word2 are the same. {
… } Note
that the above is the same as below if (word2.equals(word1)) {
… }
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|